It’s frustrating when you’re feeling afraid or uncomfortable in a social setting. Maybe your hands get sweaty before giving a big presentation or when you meet a new friend.
It’s not the most exciting thing to face a large group of strangers, but most people can make it through it. Socially anxious people have a fear of rejection, embarrassment, or negative judgment surrounding certain social conditions.
Social anxiety disorder occurs when the individual develops intense anxiety, affects personal or professional life, and lasts for at least six months. Anxiety can occur in our daily lives, such as taking a test or getting a promotion, but social anxiety disorder mainly occurs during social situations.
What is social anxiety disorder?
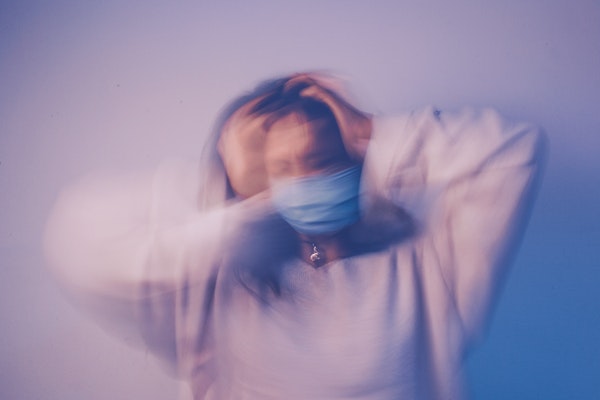
A social anxiety disorder may have strong physical signs such as increased heart rate, trembling, or feeling sick and having mental symptoms such as difficulty concentrating or a fear of being judged as a fool.
It is unlikely that the individual feels fearless or invincible despite being aware that it is excessive.
People with social anxiety disorders sometimes refer to them as social phobias, causing them to avoid social situations.
They may be unable to talk to people or attend social gatherings. They fear being judged and feel powerless to change their behavior, no matter how unreasonable the fears.
Signs of social anxiety disorder
People’s comfort level in social situations depends on personality traits and life experiences. Some people are natural introverts; others typically are outgoing. Feelings of shyness or discomfort in certain situations aren’t necessarily signs of social anxiety disorder.
The difference between social anxiety disorder and everyday nervousness is that it involves fear, anxiety, and avoidance that interferes with day-to-day activities, work, school, and social relationships. The disorder typically begins in the early to mid-teens, though it can sometimes start in younger children or adults.
There are many physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms of social anxiety disorder.
Symptoms of social anxiety include:
- physical symptoms Like blushing, sweating, nausea, trembling, and a quickened heartbeat can also occur
- Panic attacks or feelings of panic
- Anxiety or an anxiety-ridden state of mind a person experiences in the presence of others fear of experiencing anxiety or seeming anxious in front of others.
- The fear of getting judged by others.
- The feeling of discomfort or fear when dealing with guests.
- Experiencing extreme self-consciousness, embarrassment, and awkwardness when in public
- Speaking with difficulty
- An anxiety-inducing situation to avoid.
- The unyielding posture of your body and softer voice during social interaction.
- Having trouble keeping eye contact, critical thoughts, negative self-talk, and lack of self-esteem.
Symptoms caused by these conditions may lead to difficulty functioning at school and work. If they remain untreated, they may not reach their potential at work or school, as they might avoid activities such as public speaking or receiving promotions.
If social anxiety is excessive or chronic, it can lead to the onset of other mental illnesses such as depression and substance abuse problems.
How to treat Social Anxiety Disorder?
Social anxiety can be managed by taking various treatment choices to help control your symptoms, regain confidence, and overcome your anxiety.
Anxiety disorders can persist for the rest of the person’s life without treatment — but it often feels fine or more distressed at several points.
Healthcare professionals may prescribe psychotherapy or medication.
â— Medications
People who suffer from social anxiety disorder can control the symptoms through a range of medications.
â— Psychotherapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy(CBT), or talking therapy, allows people to gain insight into their experiences and improve effective coping strategies.
Preventative actions
The onset of an anxiety disorder can’t be predicted, but you can reduce the likelihood of its adverse effects if you are already anxious.
- Anxiety can be harder to treat due to a delay, so seek treatment as soon as possible.
- Maintain a journal. Regular monitoring of your personal life will assist you, and your mental health specialist in determining what is bringing you discomfort and what appears to feel good.
- Manage your time and energy to minimize anxiety by prioritizing your life matters. Do the things you enjoy doing.
- Avoid using harmful substances. Anxiety may be caused or exacerbated by the use of alcohol, drugs, or even caffeine or nicotine. Ready to quit all of these drugs will be stressful if you are dependent on them. If you cannot leave on your own, see your psychiatrist or locate a recovery facility or counseling service to assist you.