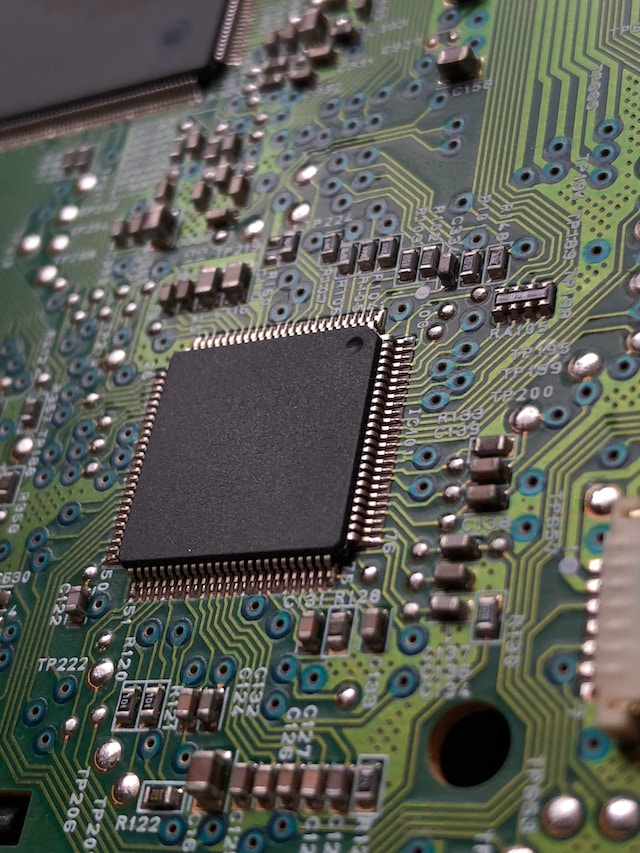
In the ever-evolving landscape of international trade, disputes and conflicts are bound to arise. One such conflict has emerged between China and the Netherlands, focusing on the export of Dutch curb chip equipment. This article delves into the details of this trade dispute, the underlying factors contributing to it, and the potential ramifications for the semiconductor industry and the bilateral relationship between the two nations.
Understanding the Dutch Curb Chip Equipment Exports:
The Netherlands has long been renowned for its expertise in the semiconductor industry, particularly in the production of curb chip equipment. These advanced machines play a crucial role in the manufacturing process of semiconductor chips, which are vital components in various electronic devices. Dutch manufacturers have been exporting these machines to countries worldwide, including China, which has become a major consumer of curb chip equipment.
Chinese Ire and Rising Tensions:
In recent months, the export of Dutch curb chip equipment to China has sparked growing tensions between the two countries. Chinese authorities have expressed their discontent and frustration with the Dutch exports, citing concerns over national security and technological autonomy. China’s semiconductor industry has been striving for self-sufficiency and reducing reliance on foreign equipment, making the import of curb chip equipment a sensitive matter.
Impact on the Semiconductor Industry:
The trade conflict has significant implications for the semiconductor industry, as the Chinese market is one of the largest consumers of curb chip equipment. Chinese companies heavily rely on advanced machinery for the production of high-quality chips to meet the demands of their domestic market. With the Dutch curb chip equipment exports facing scrutiny and potential restrictions, Chinese manufacturers might encounter challenges in sourcing suitable alternatives and maintaining production capabilities.
Bilateral Relations in the Balance:
The tensions arising from the Dutch curb chip equipment exports have strained the bilateral relationship between China and the Netherlands. Both countries have been important trade partners, with the Netherlands being a gateway to Europe for Chinese goods and investments. The trade conflict has the potential to impact other sectors and areas of cooperation between the two nations, raising concerns about the overall stability of their relationship.
Possible Resolutions and Future Outlook:
Resolving the Dutch curb chip equipment trade conflict is a complex task that requires careful consideration of both economic and political factors. Negotiations and discussions between Chinese and Dutch officials are ongoing, with the aim of finding common ground and mitigating the potential consequences of the trade dispute. The outcome of these discussions will shape the future of the semiconductor industry and the broader relationship between China and the Netherlands.
Conclusion:
The export of Dutch curb chip equipment has become a contentious issue, triggering tensions between China and the Netherlands. The conflict highlights the challenges associated with international trade, particularly in technologically sensitive sectors such as the semiconductor industry. As negotiations continue, it remains to be seen how the resolution of this trade dispute will impact the semiconductor market and the overall dynamics between China and the Netherlands.