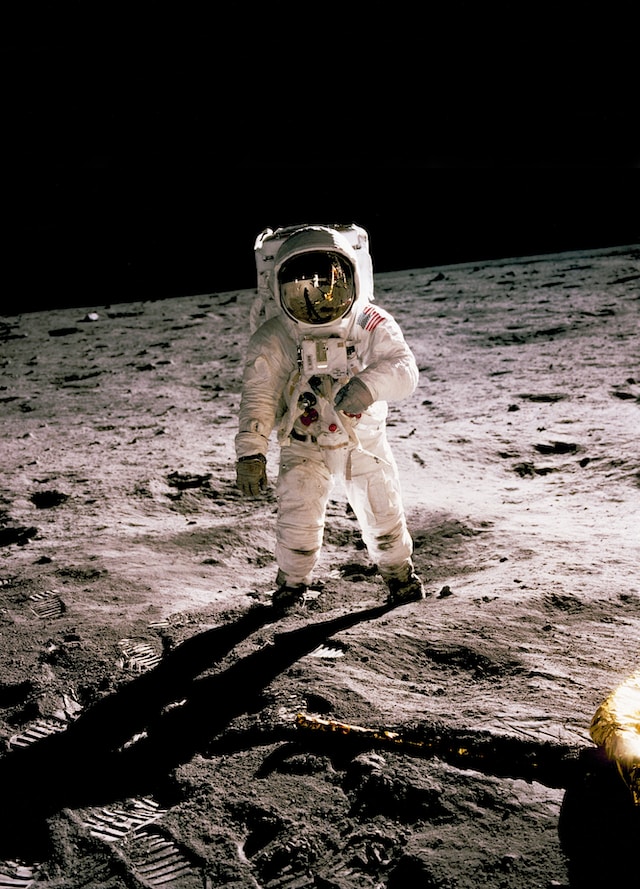
Space travel has long been a subject of fascination and exploration for humans. As we venture further into the cosmos, it becomes increasingly important to understand the effects of space on the human body, particularly on the immune system. A recent study has revealed intriguing insights into how the immune system of astronauts breaks down during their time in space. In this article, we delve into the key findings, shed light on the challenges posed by the unique space environment, and discuss the implications for future space exploration.
The Effects of Microgravity
One of the defining factors of space travel is exposure to microgravity. While this weightless environment may seem appealing, it poses several challenges for the human body, including the immune system. The study found that extended periods spent in microgravity significantly affect astronauts’ immune response, leading to a breakdown in their overall immune function.
Impaired Immune Response
The human immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from harmful pathogens and foreign invaders. However, in the absence of gravity, this system undergoes significant changes. The study revealed that certain immune cells, such as T cells, which play a crucial role in fighting infections, become less effective in microgravity. This compromised immune response leaves astronauts more vulnerable to infections and diseases.
Altered Gene Expression
Further analysis of the study’s findings revealed that space travel triggers changes in gene expression within immune cells. Genes responsible for regulating immune function showed altered activity, leading to dysregulation of the immune system. This dysregulation can persist even after astronauts return to Earth, making it essential to develop strategies for mitigating these effects.
Impact on Long-Duration Missions
With future missions planned for Mars and beyond, understanding the long-term impact of space travel on the immune system is paramount. The study suggests that as mission durations increase, so does the risk of immune system breakdown. Extended exposure to microgravity could further compromise astronauts’ health and performance, making it crucial to develop countermeasures to support their immune function during these prolonged missions.
Mitigating Strategies
Based on the study’s findings, researchers are exploring various strategies to counteract the detrimental effects of space travel on the immune system. These include targeted nutrition plans, personalized exercise regimens, and the development of pharmaceutical interventions. By enhancing immune function through these measures, astronauts may be better equipped to withstand the challenges posed by the space environment.
The Future of Space Exploration
As humanity sets its sights on ambitious space exploration endeavors, the study’s insights into immune system breakdown provide valuable knowledge for designing safer and more sustainable missions. By further investigating the mechanisms behind these changes and implementing appropriate countermeasures, scientists and space agencies can work towards safeguarding astronauts’ health and well-being during prolonged space travel.
Conclusion
The study revealing the breakdown of astronauts’ immune systems during space travel highlights the pressing need for comprehensive research and countermeasures to ensure the well-being of future space explorers. Microgravity-induced changes in immune response and altered gene expression pose significant challenges, particularly for long-duration missions. By developing strategies to mitigate these effects, scientists and space agencies can pave the way for safer and more successful journeys into the unknown.