This article explores the U.S. economic projection for December 2024, focusing on GDP growth, inflation trends, labor market conditions, Federal Reserve policy, and global pressures.
As December 2024 approaches, the U.S. economy is navigating through a period of cautious growth, with various factors influencing its performance. Projections suggest a moderate economic recovery after the pandemic-induced slowdown, accompanied by a mix of challenges and positive developments. This article offers an overview of the expected economic landscape, with a focus on key indicators like GDP growth, inflation trends, employment forecasts, and the role of fiscal and monetary policies.
GDP Growth Forecast for December 2024
The U.S. GDP growth in December 2024 is expected to remain subdued, with a forecasted growth rate of approximately 1.4%. This represents a deceleration compared to previous years but is still seen as a moderate recovery after the economic downturn caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Factors such as higher interest rates, global supply chain issues, and inflationary pressures continue to create a challenging environment for sustained, robust growth. While consumer spending and business investments are expected to contribute to growth, the pace of recovery is likely to remain below historical averages.
The U.S. economy’s GDP growth rate reflects the cumulative impact of higher borrowing costs, rising inflation, and global trade tensions. Furthermore, the slowing demand in consumer goods and housing markets suggests a gradual recovery rather than a sharp rebound. Key sectors such as technology, healthcare, and services will likely remain resilient, with strong growth in those industries providing some support for overall economic performance. Still, expectations remain tempered as businesses and consumers adjust to a more cautious economic environment.
The government’s fiscal policies, including infrastructure spending, are likely to provide additional economic support, especially in 2025. Public investment is expected to play a role in spurring economic activity, particularly in sectors like construction and technology. However, concerns over national debt and deficit spending could limit the extent to which fiscal stimulus is applied. Analysts predict that the full impact of these policies will become more apparent in 2025, as infrastructure projects and social programs are ramped up.
Despite these challenges, the U.S. economy is expected to avoid a contraction, and the growth projected for 2024 is viewed as a step forward, albeit modest. As global conditions stabilize, particularly in key trading partners, there is room for optimism regarding future economic performance. A focus on innovation and adaptation to changing global dynamics, including energy transitions and digitalization, will be critical for long-term growth beyond 2024.
In summary, the U.S. economy’s GDP growth forecast for December 2024 indicates a slow but steady recovery. While challenges remain, government policies and industry resilience provide a foundation for gradual economic improvement. This outlook sets the stage for stronger growth in the years ahead as global and domestic conditions evolve.
Inflation Trends and Projections
Inflation continues to be a primary concern for the U.S. economy in late 2024, although signs of moderation are emerging. After a period of high inflation driven by supply chain disruptions, increased consumer demand, and rising energy costs, inflation is projected to decrease gradually. By December 2024, core inflation—excluding volatile food and energy prices—is expected to stabilize around 2.4%. This represents a significant improvement compared to the previous years, when inflation surged to multi-decade highs.
A slowdown in inflation can be attributed to the Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes earlier in 2024, which have helped to cool the overheated economy. While inflation remains high in some sectors, particularly in services such as healthcare, transportation, and education, the overall trend is expected to be one of moderation. The easing of supply chain bottlenecks and the return of production capacity in key industries also contribute to this decline in price pressures.
Energy prices are another critical factor in the inflation equation. As oil prices stabilize and global production resumes post-pandemic, there is hope that energy costs will ease, contributing to lower inflation. However, fluctuations in global energy markets and geopolitical tensions could lead to periods of volatility, which would affect inflation trends. Nonetheless, for most of 2024, the impact of higher energy prices on overall inflation is expected to lessen, resulting in a more balanced inflationary environment.
Consumers are likely to feel the effects of lower inflation in their everyday spending. With rising wages and stable inflation, purchasing power is expected to improve for many households, allowing for more discretionary spending. This shift in consumer behavior could support moderate economic growth, especially in sectors like retail and services. However, inflationary pressures in certain areas may continue to challenge the budgets of low- and middle-income families.
As the year progresses, inflation is expected to gradually return to the Federal Reserve’s 2% target in the medium term, providing greater economic stability. By 2025, the effects of the Fed’s monetary policy decisions will be more visible, with inflation pressures likely to subside further. This would create a more favorable environment for business investment and consumer spending, aiding in a more robust recovery.
In conclusion, while inflation remains a concern in the short term, projections for December 2024 suggest a downward trend. As the Federal Reserve’s actions take effect and global economic conditions stabilize, inflation should moderate, helping to alleviate financial pressure on U.S. households and businesses.

Labor Market Outlook
The U.S. labor market remains relatively resilient despite the economic uncertainties of 2024. Unemployment is expected to remain relatively stable, hovering between 4% and 4.5% by the end of the year. The job market has been supported by strong demand in industries such as technology, healthcare, and logistics, which continue to thrive. However, the pace of job growth is expected to slow as businesses adjust to higher interest rates and a more cautious economic climate.
Despite the slowdown, certain sectors are expected to continue hiring at a robust pace. In particular, healthcare, technology, and renewable energy industries will remain in high demand as they align with long-term trends in the economy. The shift toward digital transformation, remote work, and green energy policies is creating a structural shift in the types of jobs available, with more positions in tech and healthcare and fewer in traditional sectors like retail and manufacturing.
Wage growth is another critical factor in the labor market outlook. With inflation pressures easing, real wage growth is expected to stabilize, although wages in certain industries, particularly those that are technology-driven or in high demand, will likely continue to see strong increases. This wage growth, combined with a steady labor market, will provide some financial relief for workers, especially in high-demand sectors.
However, job market dynamics are not uniform across all demographics. Certain groups, including younger workers and those without advanced degrees, may continue to face challenges in securing stable employment. Additionally, industries that are more sensitive to interest rate changes, such as housing and construction, may see reduced hiring as borrowing costs remain elevated. The shift toward automation and AI in some sectors also presents both opportunities and challenges for the labor force.
In summary, the U.S. labor market in December 2024 is expected to be stable but with slower job growth due to higher interest rates and economic adjustments. While certain sectors will continue to thrive, overall employment growth will be more modest as businesses remain cautious about expansion.
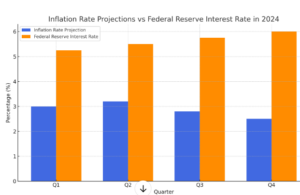
Federal Reserve and Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve’s policies regarding interest rates are a central factor in the U.S. economic outlook for December 2024. Following a series of interest rate hikes earlier in the year, the Fed is likely to keep rates high through the end of 2024 in an effort to control inflation. Higher borrowing costs have already begun to slow down consumer spending and business investment, particularly in interest-sensitive sectors like real estate and durable goods.
The decision to raise rates was driven by the need to combat persistent inflation, which reached its highest levels in decades. By tightening monetary policy, the Federal Reserve aims to reduce demand in the economy, thereby cooling inflationary pressures. However, the impact of these rate hikes on economic growth is becoming more apparent, with slower expansion expected in 2024 as a result of reduced consumer borrowing and business investment.
The Fed’s actions have also had an effect on the housing market, where mortgage rates have risen sharply. Higher mortgage rates have cooled the housing market, leading to fewer home purchases and less construction activity. While this may reduce inflationary pressures in the housing sector, it also means slower economic growth in related industries, such as construction and home improvement.
By the end of 2024, the Fed may start considering reducing interest rates if inflation continues to subside and economic conditions stabilize. Lower rates could help stimulate borrowing and investment, supporting economic growth in 2025 and beyond. However, the Fed’s decision will depend on the evolution of inflation and other economic indicators. The central bank’s cautious stance is expected to persist in the short term, with any interest rate cuts likely delayed until 2025.
In conclusion, the Federal Reserve’s interest rate policies will remain a critical factor in the U.S. economy’s performance through December 2024. Higher rates have already slowed certain sectors, but with inflation easing, the Fed may consider reducing rates in 2025 to support further economic recovery.
Global Economic Pressures and Trade
The U.S. economy is also significantly influenced by global economic conditions, which continue to be a source of uncertainty. Geopolitical tensions, particularly in Europe and Asia, have disrupted global trade flows and contributed to rising energy prices. These factors have compounded inflationary pressures and contributed to a more complex economic environment in 2024.
Global supply chain disruptions, caused by factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic, labor shortages, and geopolitical instability, have had a lasting impact on the U.S. economy. While supply chains are slowly recovering, disruptions in key industries like electronics, automotive manufacturing, and raw materials continue to affect U.S. businesses. Additionally, trade restrictions and tariffs imposed by other nations, particularly China, have had a negative impact on U.S. exports, further slowing economic growth.
Despite these challenges, the U.S. economy benefits from a diversified trade network. As global economic conditions improve, U.S. businesses will likely benefit from stronger demand in key markets, particularly in Asia and Europe. Moreover, the increasing focus on renewable energy and sustainable technology may open new avenues for trade and investment, providingU.S. Economic Projection for December 2024: A Modest Recovery
As December 2024 approaches, the U.S. economy faces a complex landscape of challenges and opportunities. In this article, we examine key indicators that will shape the economic outlook, including GDP growth, inflation, employment trends, Federal Reserve policy, and global economic pressures.
GDP Growth Forecast for December 2024
The U.S. economy is projected to experience modest growth in December 2024, with a forecasted GDP growth rate of approximately 1.4%. This marks a deceleration from previous years but reflects the economy’s slow recovery following the pandemic. Factors such as rising interest rates, global supply chain issues, and inflationary pressures are limiting more robust growth. While sectors like healthcare, technology, and services may continue to expand, the overall pace of recovery will be restrained.
A key aspect of this forecast is the balance between consumer spending and business investment. Consumer demand remains strong in certain sectors, but the increased cost of borrowing has led businesses to scale back investments. Global uncertainties, including trade disruptions and geopolitical tensions, further contribute to a cautious outlook.
Nevertheless, the GDP growth rate of 1.4% represents progress from the previous economic downturn, indicating a steady but unspectacular recovery. The U.S. government’s fiscal policies, including infrastructure spending, will play a crucial role in supporting growth. However, concerns over national debt may limit the scope of stimulus spending in the near future.
By the end of 2024, it is expected that the economy will remain on a path of gradual recovery, with a more noticeable rebound occurring in 2025 as global conditions stabilize and fiscal stimulus initiatives take effect.
Inflation Trends and Projections
Inflation continues to be a primary concern for the U.S. economy as it progresses into late 2024. After a period of sharp inflation caused by supply chain disruptions and rising demand, inflation is projected to ease gradually. By December 2024, core inflation (excluding food and energy) is expected to stabilize at around 2.4%. This marks a significant improvement compared to the multi-decade highs seen earlier in the year.
A key driver of this moderation is the Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes, which have successfully cooled the economy. While inflation pressures will persist in sectors like healthcare and education, the overall trend is expected to be one of stabilization. The easing of supply chain bottlenecks and improved production capacity in key industries will also contribute to the decline in inflationary pressures.
Energy prices, which have been volatile in recent years, are expected to stabilize in the coming months. As oil production recovers globally, the cost of energy will likely ease, helping to mitigate inflation. However, geopolitical factors and unforeseen disruptions could lead to fluctuations in energy costs, which would affect inflation in the short term.
For consumers, lower inflation means increased purchasing power and a more stable cost of living. With real wages rising and inflation moderating, households will likely see some relief in their finances, supporting continued spending in sectors like retail and services.
In conclusion, while inflation remains a concern, the December 2024 outlook points toward a gradual reduction in price pressures. This would create a more favorable environment for economic stability in the short term and growth in the longer term.
Labor Market Outlook
The U.S. labor market in December 2024 is projected to remain stable, with the unemployment rate expected to hover between 4% and 4.5%. While job growth is likely to slow down due to higher interest rates, sectors like healthcare, technology, and renewable energy will continue to experience strong demand. These industries are expected to hire at a steady pace as the economy adapts to post-pandemic conditions.
In the face of a more cautious economic climate, businesses are expected to focus on efficiency and technological investments. While some job losses are anticipated in interest-sensitive sectors like housing and construction, there are also opportunities for growth in jobs that align with long-term trends, including digital transformation and green energy.
Wages are projected to grow in certain sectors, particularly in technology and healthcare, where demand for skilled workers remains high. While wage growth will not be as robust across the board, real wage increases should help improve living standards for many workers. However, challenges persist for lower-income workers and those without advanced qualifications, as these groups may face difficulties in securing stable employment.
Despite these concerns, the labor market remains relatively resilient compared to other advanced economies, with structural changes and skill shifts driving employment in high-demand sectors. As businesses adjust to higher borrowing costs and slower consumer demand, job growth is likely to be more modest than in previous years.
Overall, the labor market is expected to remain stable in December 2024, with growth concentrated in sectors aligned with technological innovation and sustainability.
Federal Reserve and Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve’s policies will play a pivotal role in shaping the U.S. economy through December 2024. In response to persistent inflation, the Fed has already raised interest rates multiple times during the year. These higher rates have begun to slow down consumer borrowing and business investment, particularly in housing and durable goods. The Fed’s decision to keep interest rates high is expected to continue throughout the year as it works to bring inflation under control.
While higher rates have cooled some sectors of the economy, the Fed’s actions have been essential in preventing inflation from spiraling further. However, there are concerns that the extended period of higher rates may slow down economic growth too much, causing a potential recession in the future.
The housing market has already experienced the effects of these rate hikes, with higher mortgage rates dampening home purchases and construction activity. While this cooling effect may help reduce inflation in the housing sector, it also means slower growth in related industries. The manufacturing and construction sectors may also face challenges as financing becomes more expensive.
The Fed’s cautious approach to interest rate cuts is expected to persist into 2025. A reduction in rates is contingent on further easing of inflationary pressures and stabilization of the economy. For now, the focus remains on managing inflation through higher rates.
Global Economic Pressures and Trade
Global economic conditions continue to exert pressure on the U.S. economy. Geopolitical tensions, trade disruptions, and rising energy prices have added layers of complexity to the economic landscape. In particular, the trade relationship with China and other nations remains uncertain, with tariffs and trade restrictions potentially slowing down U.S. exports.
Supply chain disruptions have also contributed to slower economic growth, especially in industries reliant on imports such as electronics, automotive manufacturing, and raw materials. However, the easing of some global supply chain issues and the return of production in key industries will help reduce these pressures as 2024 progresses.
The global demand for U.S. exports is expected to stabilize, particularly in markets like Asia and Europe. Additionally, there may be new opportunities for U.S. businesses in the renewable energy and technology sectors, driven by the global shift toward sustainability and digitalization.
Despite these challenges, the U.S. economy’s diversification and resilient sectors should enable it to weather global economic pressures. With key trading partners beginning to recover, trade volumes are expected to increase in 2025, contributing to a gradual economic rebound.
In conclusion, the U.S. economy’s outlook for December 2024 remains shaped by both domestic policy and global economic trends. While the country faces challenges such as high inflation, slower job growth, and global trade disruptions, its diversification and adaptation to new industries should help drive moderate recovery. Looking forward, the economy is poised for gradual improvement as key factors, such as inflation and global trade, stabilize.
FAQ:
- What is the U.S. GDP growth forecast for December 2024?
The U.S. GDP is projected to grow at 1.4% by December 2024, indicating a modest recovery from the pandemic downturn. - How will inflation affect the U.S. economy in December 2024?
Inflation is expected to stabilize at around 2.4%, with easing energy prices and the Federal Reserve’s actions contributing to this moderation. - What is the expected unemployment rate by December 2024?
Unemployment is projected to remain steady between 4% and 4.5%, with slow job growth concentrated in sectors like technology and healthcare. - Will the Federal Reserve cut interest rates in December 2024?
It is unlikely, as the Fed is expected to maintain higher rates throughout 2024 to control inflation, with rate cuts anticipated only in 2025. - What global factors are influencing the U.S. economy?
Global trade tensions, energy price fluctuations, and supply chain disruptions continue to affect U.S. exports and inflation trends.













